Integrated environmental monitoring system using
information and telecommunications technologies
Ken-ichiro Muramoto, Ph. D., Professor |
 |
Environmental phenomena often exhibit different characteristics depending
on the scale of the observations. To detect environmental changes, determination
of spatial and temporal resolution is important.
Precipitation is a very important part of climate. This includes rain,
snow, graupel, mist, etc. The form of precipitation depends on the source
cloud and the temperature of the air below the cloud. Changes in the amount
of precipitation falling to Earth affect our lives in many ways.
Since forests play an important role in keeping environmental conditions
suitable for life on Earth, management and protection of forest resources
are important. Even though vegetation varies largely in spatial and temporal
scales, there are signs of rapid degradation in East Asia due to human
activities and which affect the climate. Quantitative information on vegetation
coverage is important for a global-change research.
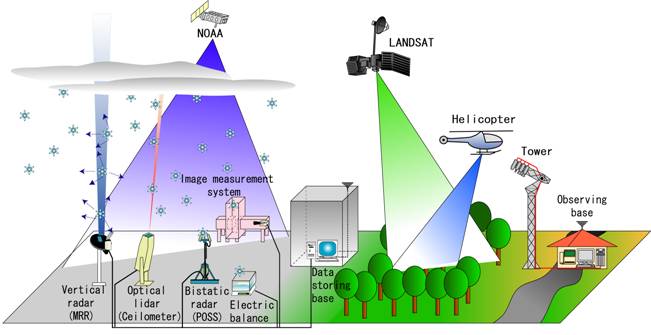
To monitor meteorological and vegetation characteristics, we conduct
research by using several kinds of sensing systems and satellite imagery.
Though remote sensing is a useful tool for obtaining data over large areas,
there are problems in methodology and accuracy to overcome for the technique
to be utilized successfully. Therefore, it is emphasized that in situ observation
remains essential when applying remote sensing techniques.
We have strong links between field and laboratory experimentation, remotely
sensed data analysis, computer modeling and geographic information systems
(GIS) in its research. Advances made in the information and telecommunication
technology will lead to development of environmental monitoring systems
with integrated remote sensing and in situ observations.